Quick answer
Knowing how to create a sales strategy is essential for any organization looking to grow revenue and outperform competitors. It involves many moving parts that influence results, so it is vital to get it right. Consider using mapping software in your research and data analysis stages. Nothing beats visual intelligence when making complex decisions.
Key takeaways:
- Teams using location-based sales planning see up to 30% higher rep productivity through optimized routing and territory design, and achieve better territory balance, reducing rep burnout.
- Mapping tools help surface white space opportunities by showing exactly where competitors are concentrated, and where they’re not.
- You can segment customers geographically to build high-conversion buyer personas based on real behavior and market conditions.
- Visualizing sales pipeline data on a map reveals slow-moving regions and missed opportunities that spreadsheets often hide.
- Real-time map updates allow your team to adapt quickly to market shifts, from economic changes to competitor moves.
Why Use Mapping Software in Sales Strategy
Geography impacts everything in sales, from where customers are located to how efficiently your team can reach them. Software for mapping business data helps uncover these geographic dynamics by making customer and sales data visual and interactive.
When creating a sales strategy, maps expose opportunities and gaps you might miss in spreadsheets. They help connect the dots between market potential, rep coverage, and customer demand, so your strategy is built on facts, not assumptions.
Step-by-step Guide to Creating
a Sales Strategy
Creating a strong, data-informed strategy starts with understanding your market landscape. Here’s how to create a sales strategy plan using a mapping solution, step by step.
Step 1
Define Your Target Markets and Sales Territories
Start by identifying where your best opportunities lie. Import customer, lead, and market data into your advanced mapping software tool to highlight high-performing regions.
You can use this insight to create a sales strategy prioritizing territories based on revenue potential, existing customer density, and underserved zones. This will lead to a more balanced and productive sales operation.
Step 2
Identify How You Will Compete in Each Market
Every market is different. Use maps to analyze regional trends, customer behaviors, and economic indicators. This lets you tailor your approach for each area, whether you're competing on speed, service, or specialization.
Location-based data ensures your differentiation strategy aligns with on-the-ground realities, not just assumptions. Use pin maps to show your competitors' locations and give more insight into your analysis.
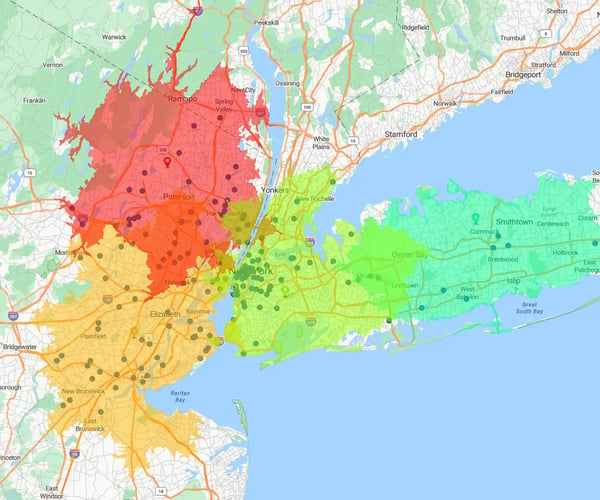
Step 3
Map and Analyze Competitor Locations
Knowing where your competitors are helps you find white space. Use mapping tools to visualize competitor store locations, rep territories, or service areas.
By comparing this data with yours, you can spot market gaps, saturation zones, and areas where you're best positioned to win. These are key inputs when creating a sales strategy plan that delivers growth.
Step 4
Build Buyer PersoNAS and Ideal Customer Profiles
Your best customers often share common geographic traits. Use mapping tools to segment and analyze your existing clients by location, industry, size, or behavior.
These insights help refine buyer personas and ideal customer profiles, making your outreach more focused and your message more relevant. This is essential when learning how to create a sales strategy that converts.
Here are some typical steps:
- Problem recognition: What were the triggers that resulted in a change of mind that initiated their process?
- Research: How do they research service providers?
- Onboarding: When and how do they select potential partners?
- Clarify preferences: When and how do they narrow their selection criteria?
- ROI analysis: When and how will they measure and calculate ROI, and how do you meet their needs?
- Engage: What are the final steps to agreeing on a sales deal with your organization?
Step 5
Align the Sales Process With Location Data
Mapping programs let you overlay your sales funnel or pipeline data onto territories. This reveals bottlenecks, slow regions, or areas with untapped potential.
For more guidance, check out our blog on how to design a sales process, which complements this step by helping you align your internal workflows with location-based insights.
With this view, you can align sales tactics to local realities, adjusting rep efforts, channel strategies, or marketing support to match regional trends and boost conversions.
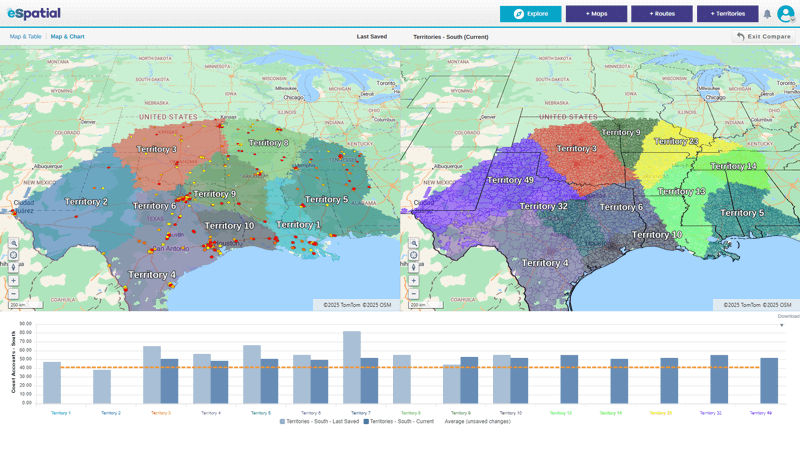
Step 6
Design and Optimize Sales Territories
Poorly drawn territories lead to inefficiencies and missed targets. Use mapping or explore territory management software features to build balanced, data-driven territories based on opportunity, travel time, and rep availability.
Territory optimization ensures equitable workloads and improves morale, making it a critical component of an effective and scalable sales strategy.
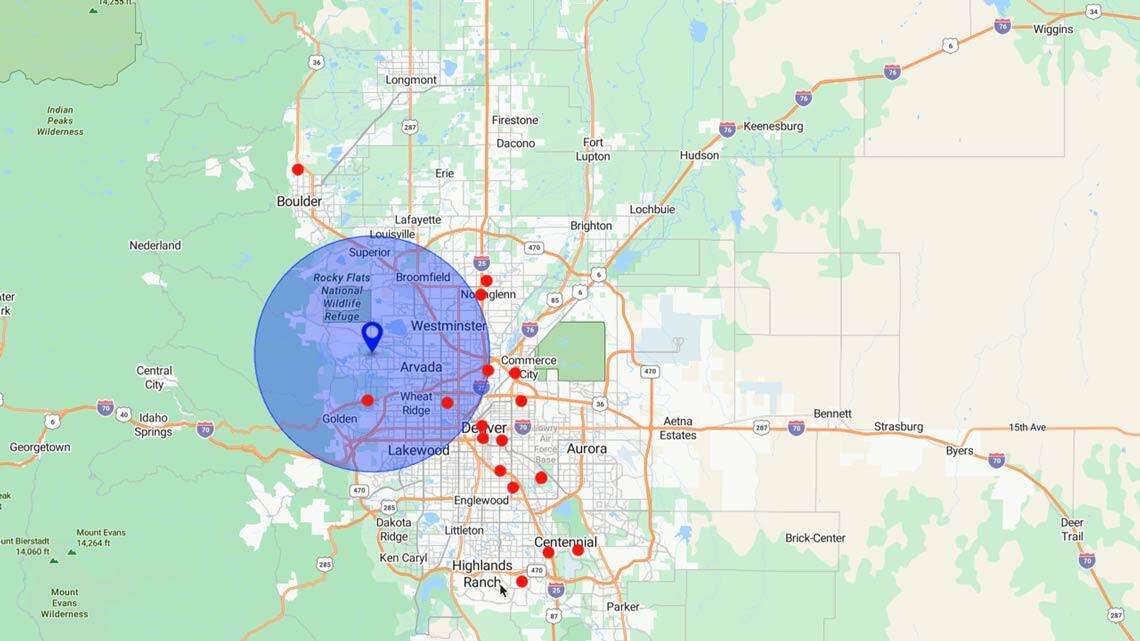
Step 7
Improve Routing and Field Sales Efficiency
Location data isn't just for planning; it also boosts execution. Geospatial mapping software allows reps to plan smarter routes, minimize travel, and visit more customers per day.
Whether you’re in field sales or service delivery, optimized routing saves time, cuts costs, and boosts productivity. Creating a sales strategy with mapping tools is one of the most practical wins.
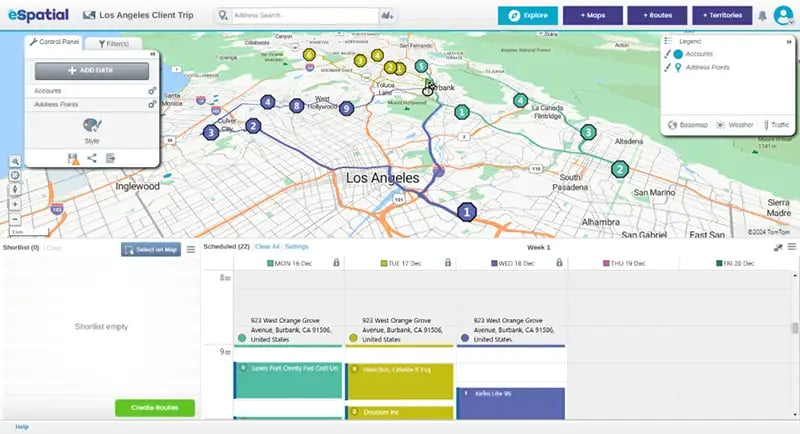
Benefits of a Map-driven Sales Strategy
Sales strategies built on maps offer several competitive advantages. Here are the most impactful:
- Data clarity: Visualizing your customer and market data simplifies complex decisions.
- Faster insights: Identify trends and patterns at a glance, without digging through reports.
- Improved performance: Balanced territories and smarter routing boost team productivity.
- Stronger targeting: Reach the right customers, in the right place, at the right time.
- Agility: Quickly adapt to market changes by updating maps in real time.
These benefits make location intelligence a must-have when learning how to create a sales strategy that outpaces the competition.
Best Practices for Using Mapping
Programs in Sales Planning
These practices make creating a sales strategy more streamlined, scalable, and responsive. To get the most out of mapping tools, follow these tips:
- Start with clean data: Ensure customer, lead, and territory data are accurate and up to date.
- Layer datasets: Combine internal performance data with external market or demographic layers for deeper insight.
- Collaborate cross-functionally: Share maps with sales, marketing, and leadership to align decisions.
- Review regularly: Sales landscapes shift—review your maps quarterly to stay ahead.
- Invest in training: Ensure your team understands how to use mapping tools effectively.
Final Thoughts on Creating a Sales
Strategy With Mapping Tools
In today's data-driven landscape, knowing how to create a sales strategy is only part of the equation. The real differentiator lies in applying tools like mapping software to make smarter, faster, and more grounded decisions. Whether you're refining your go-to-market approach, adjusting territories, or increasing field sales productivity, maps help you build a modern strategy anchored in location intelligence.
Ready to get started? Explore pricing for mapping solutions and see how easy it is to start building a more brilliant sales strategy today. Use this guide to kickstart your process of creating a sales strategy plan that doesn't just look good on paper but performs in the real world.