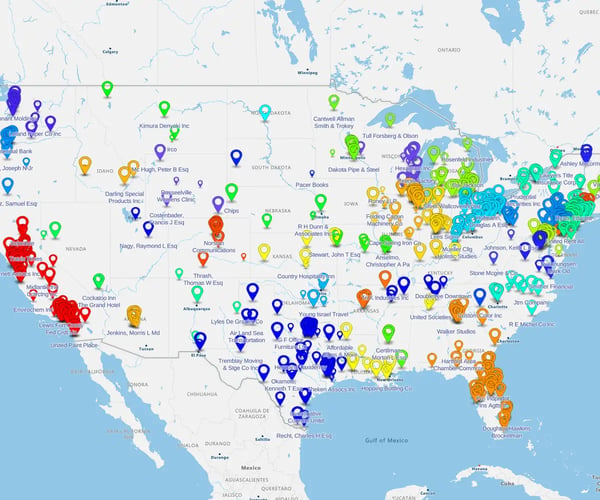
Quick answer
Spatial mapping turns raw geospatial data into dynamic, digital visualizations that outperform static traditional maps. It transforms abstract geography into actionable business intelligence, helping industries from healthcare to finance solve complex problems faster.
- Optimize operations: Streamlines route planning and logistics to cut costs
- Analyze markets:: Pinpoints prime real estate sites and visualizes customer density
- Detect patterns:: Spots anomalies instantly, like fraud clusters or health outbreaks, that spreadsheets miss
Spatial mapping captures and displays geospatial data to visualise business operations, customers, and assets.
It turns abstract data into location-based insights. You move beyond static spreadsheets to see where your business actually happens.
The big picture: Maps have evolved from ancient parchment to interactive digital tools. This guide breaks down:
- How geospatial mapping works
- Which industries it revolutionizes
- Steps to create your own map for analysis
What is spatial mapping?
Spatial mapping is the digital visualization of geographical data. It transforms raw datasets—from GPS, satellites, or surveys—into a navigable virtual world.
How it works:
- Collect: Gather data on real-world locations and assets
- Geomap: Assign geographic identifiers to that data
- Display: Render the information on a dynamic digital platform
Why it matters: This technology powers daily tools like your phone's GPS and critical tasks like engineering bridges. It solves complex mobility, infrastructure, and environmental issues that static paper maps simply cannot handle.
Use Cases for Spatial Mapping
Spatial mapping revolutionises industries by digitising environments for precise location tracking. It drives innovation where accuracy is non-negotiable.
Healthcare: Visualizing Care
Spatial mapping transforms patient demographics and clinical data into interactive visualisations.
Providers can identify trends and compare patterns instantly. It moves beyond data entry to data action, directly improving patient service.
eSpatial layers these complex datasets for healthcare to clarify insights and drive better care.

Tech and Software: Optimizing Operations
Tech and software use location analytics to drive efficiency across infrastructure, sales, and product development.
How it works
- Field ops: Map technician territories to allocate resources and prioritise jobs
- Sales: Optimise routes to maximise time with customers and cut travel costs
eSpatial’s territory and routing software ensures field staff spend their day working, not driving.

Financial Services: Mitigating Risk
Spatial mapping converts financial data into location intelligence to uncover opportunities and reduce exposure. Banks use location data to visualise asset risk, manage loan portfolios, and detect fraud patterns that spreadsheets miss.
The impact
- Risk & Compliance: Ensure regulatory reporting accuracy and visualize economic impact
- Lending: Assess real estate locations for smarter portfolio management
- Growth: Optimize manager territories to target new business
eSpatial’s market analysis software maps customer behaviour against risk factors instantly for financial services.
Real Estate: Pinpointing Value
Spatial maps give real estate professionals accurate, data-driven insights into property markets.
Why it matters: Integrating specific datasets allows you to uncover trends and competitive gaps that standard listings miss. Location intelligence turns "gut feeling" into evidence.
Key applications
- Site Selection: Identify high-potential locations instantly
- Valuation: Analyze market trends for precise pricing
- Sales & Leasing: Visualize assets to close deals faster
eSpatial mapping software for real estate provides the visual representation and market analysis needed to dominate the search.

Manufacturing: Supply Chain Resilience
In a volatile economy, manufacturers need locational visibility to avoid bankruptcy and drive strategy.
Why it matters: Spatial mapping turns supply chain complexity into clear, actionable insights. It helps you understand demand patterns and customer behavior at a glance.
Key benefits
- Optimization: Position warehouses and route deliveries to slash logistics costs
- Forecasting: Use location data to predict demand and manage inventory
- Risk Management: Identify bottlenecks and location issues before they impact delivery
With mapping software for manufacturers, you gain 360-degree visibility to secure your logistics.

Construction: Building Smarter
Spatial mapping is instrumental for planning, site analysis, and risk management in construction. It moves beyond blueprints to analyze the ground truth. Tools assess topography, geology, and soil composition to ensure site suitability before you break ground.
Key applications
- Site Analysis: Visualize soil and groundwater conditions to determine feasibility
- Risk Management: Identify potential disaster zones and environmental factors early
- Project Management: Design infrastructure networks with precise geographic context
Specialized mapping software for construction changes the game.
How to Create a Geospatial Map
A complete map combines mapping, visualization, and analysis on a digital platform. While the specific process varies based on your goals, one rule is constant.
The reality check: The quality of your insights relies entirely on the quality of your input data.
Step 1
Define Your Objective
Before you build, define why you need this map to establish your priorities.
Define the following
- The Questions: What specific problems must the map answer?
- The Audience: Who are they and what do they need?
- The Requirements: What data layers and display techniques are essential?
- The Success Metrics: How will you measure the map's impact?
Step 2
Select Your Mapping Software
Not all tools are created equal. Ensure your chosen software aligns with your specific data goals to future-proof your investment.
The checklist
- Capabilities: Can it build the specific maps you need, such as heat, drivetime, territory or route maps?
- Compatibility: Does it easily ingest your existing data formats?
- Innovation: Is the vendor committed to updates, or is the tool stagnant?
- Trust: Do client reviews back up the sales pitch?
Step 3
Collect and Prepare Data
Quality data is the bedrock of insightful analysis. Without accurate inputs, your visualization fails.
The workflow
- Identify: Target specific datasets, such as location coordinates and addresses
- Compile: Aggregate data from spreadsheets, databases, or existing GIS files
- Clean: Verify that the data is complete, accurate, and uniform
- Structure: Assign unique identifiers and standardize address fields for precise geocoding
Step 4
Set Parameters
Correct parameters prevent distortion and ensure your spatial analysis is accurate.
The checklist
- Align: Set parameters to match your specific objectives
- Contextualize: Choose a base map that provides the right spatial context for your region
Step 5
Analyze Results
This is the moment of truth. Use your final map to verify if you met your objectives.
The action plan
- Review: Visually inspect the map for clarity and accuracy
- Quantify: Use analysis tools to extract hard data and insights
- Compare: Layer different datasets to spot correlations
- Investigate: Flag hotspots or anomalies that require a deeper dive
- Export: Save your findings for validation and documentation
Mapping Solutions For
Businesses From eSpatial
Are you seeking advanced spatial analytics tools to help your business glean deep insights from location data through heat mapping and routing? Our eSpatial mapping software helps visualize your Excel, CRM, or ERP data for better business decisions through actionable insights.
Getting clear insights from data is an extremely reliable way to improve business operations, which is why every business that pulls data from varied sources could benefit from spatial mapping to improve operations, predict trends, serve customers better, and reduce risks, among other advantages.
Healthcare, construction, real estate, manufacturing, tech, and software are just some of the industries that benefit from mapping solutions. Don’t let your data go unutilized. Learn how our customizable mapping software solutions can support your unique needs, from scalable data management to customizable analytics dashboards. Contact us today to start optimizing your business with spatial mapping.
Frequently Asked Questions
My Team Spends Hours in Spreadsheets Trying to Analyze Location Data, but We're Not Getting Clear Insights. How is Using Spatial Mapping Fundamentally Different From the Pivot Tables and Charts We're Already Using in Excel?
Spatial mapping is fundamentally different because it transforms spreadsheet data into visual insights on a map, instantly revealing patterns and opportunities that static rows and columns hide.
That's a very common challenge when relying on Excel for planning. While spreadsheets are great for organizing data, they can't answer the crucial "why of where." Spatial mapping turns your numbers into a dynamic, visual layer. Instead of just seeing data points, you see customer clusters, territory gaps, and market trends in seconds. It’s the difference between looking at a list of addresses and seeing exactly where your biggest opportunities are, allowing you to make confident, data-backed decisions instead of educated guesses.
I Use Power Bi, but It’s Hard to Get Real Location Insights; It's More Like Just Putting Dots on a Map. How Does Your Spatial Analysis Provide Deeper Insights That a Standard Bi Tool Can't?
Unlike standard BI tools that just place dots on a map, eSpatial is a dedicated location intelligence platform that provides deeper spatial analysis, like drive-time calculations and white-space analysis.
That's a common challenge, as many BI tools have mapping features but lack analytical depth. eSpatial is built specifically for location intelligence. This means you can go far beyond simple visualization to perform advanced analysis. For example, you can create balanced territories based on drive time, identify "white space" in the market where your competitors are but you aren't, or analyze customer catchments around your locations. It's designed to give you actionable answers to complex location-based questions, not just a prettier picture of your data.
I Need to Plan Our Field Service Routes, but Just Looking at Addresses on a List Doesn't Account for Drive Time or Territory Balance. How Can I Use Spatial Mapping to Create Truly Optimized and Efficient Routes for My Team?
Spatial mapping creates optimized routes by using real-world data like drive times and traffic patterns to balance workloads, ensuring your team has the most efficient and fair plan possible.
You've hit on a key problem with manual planning. A list of accounts doesn't reflect the reality your team faces on the road. With spatial mapping, you can build territories and routes using these real-world factors. You can automatically balance territories not just by the number of accounts, but by the actual workload involved, including travel. This ensures every team member has an equitable and achievable plan, cutting down on wasted fuel and maximizing time spent with customers.
We're Planning a Series of Regional Marketing Events, and I Need to Pick Locations With the Highest Concentration of Customers and Prospects. How Can I Quickly Visualize This Data to Find the Optimal Event Locations Instead of Just Guessing?
You can find the optimal event locations by plotting your customer and prospect data on a map, using tools like heatmaps to instantly visualize geographic hotspots and make a data-backed decision. Guessing is expensive and risky, especially when planning campaigns or events6. Spatial mapping removes that uncertainty. You can instantly plot your customer and prospect data from your CRM or a spreadsheet onto a map. Using tools like heatmaps, you can immediately see the geographic "hotspots" where your target audience is most concentrated7. This allows you to choose event venues with confidence, knowing you've selected a location based on hard data, not just a hunch.
My Company is Expanding Into a New State, and I'm Responsible for the Hiring Plan. How Can Spatial Mapping Help Me Identify Where the Best Talent Pools Are and Analyze Competitor Locations to Make a Strategic Hiring Decision?
Spatial mapping helps you make a strategic hiring decision by visualizing multiple data layers at once—such as talent pools from your ATS, competitor locations, and local demographics—on a single, interactive map.
This is a perfect use case for moving from reactive to proactive workforce planning. Instead of operating with strategic blind spots9, spatial mapping allows you to see the complete talent landscape. You can map candidate data from your Applicant Tracking System (ATS), overlay it with competitor locations, and even integrate third-party data on talent density. This gives you a clear, visual picture, helping you pinpoint the best areas for recruitment and make a compelling, data-driven case for where to focus your hiring efforts.
My Operations and HR Data is Scattered Across Our CRM, an HRIS, and Multiple Spreadsheets. I'm Worried That Getting It All Into a New System Will Be a Massive It Project. How Do You Make It Easy to Integrate and Map Data From Different Sources?
eSpatial makes integration easy by design, offering seamless connections to systems like Salesforce and allowing for simple data uploads from spreadsheets, which minimizes the need for IT involvement.
That fear is completely valid; no one wants a heavy, complex implementation11. eSpatial is designed to be an agile layer that sits on top of your existing systems rather than replacing them. We solve the problem of disconnected data by offering seamless integration with platforms like Salesforce and making it simple to upload data directly from Excel in just a few clicks. The goal is to empower you to blend and visualize data from multiple sources yourself, without creating a dependency on IT for every single analysis.
I'm Concerned My Team Doesn't Have the Technical Skills for a Complex Analytics Tool; They’re Marketers and HR Planners, Not Data Scientists. How Intuitive is Your Platform for Non-technical Users to Actually Adopt and Use for Making Decisions?
Our platform is highly intuitive for non-technical users because it was designed for business teams, featuring a simple visual interface and supported by a full onboarding and success program.
This is a common concern about adopting a new tool. We build for business users, not data scientists. Your team's expertise is in marketing or HR, and our job is to give them a tool that feels intuitive to them. Our platform uses a clear, visual interface that makes complex analysis as simple as a few clicks. More importantly, we partner with you through our onboarding and customer success programs to ensure your team feels confident and gets value from day one. The focus is always on enabling your team to make better decisions, not forcing them to become software experts.
My VP Needs to See the "so What" Behind the Data, but My Charts Don't Always Land. How Does Presenting My Marketing or Workforce Plans on a Map Help Me Tell a More Persuasive Story and Get Faster Buy-in for My Strategic Recommendations?
Presenting your plans on a map helps you get faster buy-in because a map is a universal language; it transforms complex data into a clear, visual story that leadership can understand instantly.
It's a common struggle to present compelling visuals to leadership. A map is a powerful storytelling tool that solves this. Instead of showing a spreadsheet with sales numbers by ZIP code, you can present a heatmap that immediately shows which regions are performing well and which are underserved. This visual clarity shifts the conversation from trying to interpret the data to deciding what to do about it. It helps you present a compelling, undeniable case for your recommendations, leading to faster, more confident buy-in.